Learn how to do WordPress Migration safely without losing rankings or data.
What Is WordPress Migration?
WordPress migration is the process of moving a WordPress website from one location to another. Specifically, this can involve transferring between hosting providers, migrating from a different platform to WordPress, or upgrading from an outdated WordPress installation to a new one.
Moreover, a complete migration involves moving all website files, databases, media assets, and configurations. At the same time, you need to preserve functionality, SEO rankings, and user experience. For this reason, the official WordPress documentation provides foundational guidance. However, professional migrations require more comprehensive approaches.
Why Businesses Migrate to WordPress
Currently, over 810 million websites use WordPress worldwide. In fact, that’s 43% of all websites on the internet. Consequently, businesses migrate to WordPress for several concrete reasons:
Cost Reduction:
- First, proprietary platforms charge ongoing licensing fees ranging from $500 to $5,000 annually
- In contrast, WordPress is free and open-source
- As a result, you get significant long-term savings on platform costs
Performance Improvements:
- Notably, modern WordPress installations with proper optimization load in under 2 seconds
- On the other hand, legacy platforms often exceed 5-7 seconds
- Therefore, faster sites mean better user experience and conversions
SEO Capabilities:
- Additionally, WordPress offers native SEO advantages, including a clean code structure
- Furthermore, mobile responsiveness is built in
- Plus, extensive plugin options exist for advanced optimization
Flexibility:
- Remarkably, over 60,000 plugins are available
- Similarly, 10,000+ themes provide unlimited customization options
- Best of all, no need for expensive custom development
Types of WordPress Migration
Understanding the different migration types helps you prepare appropriately. Each type has unique challenges and requirements.
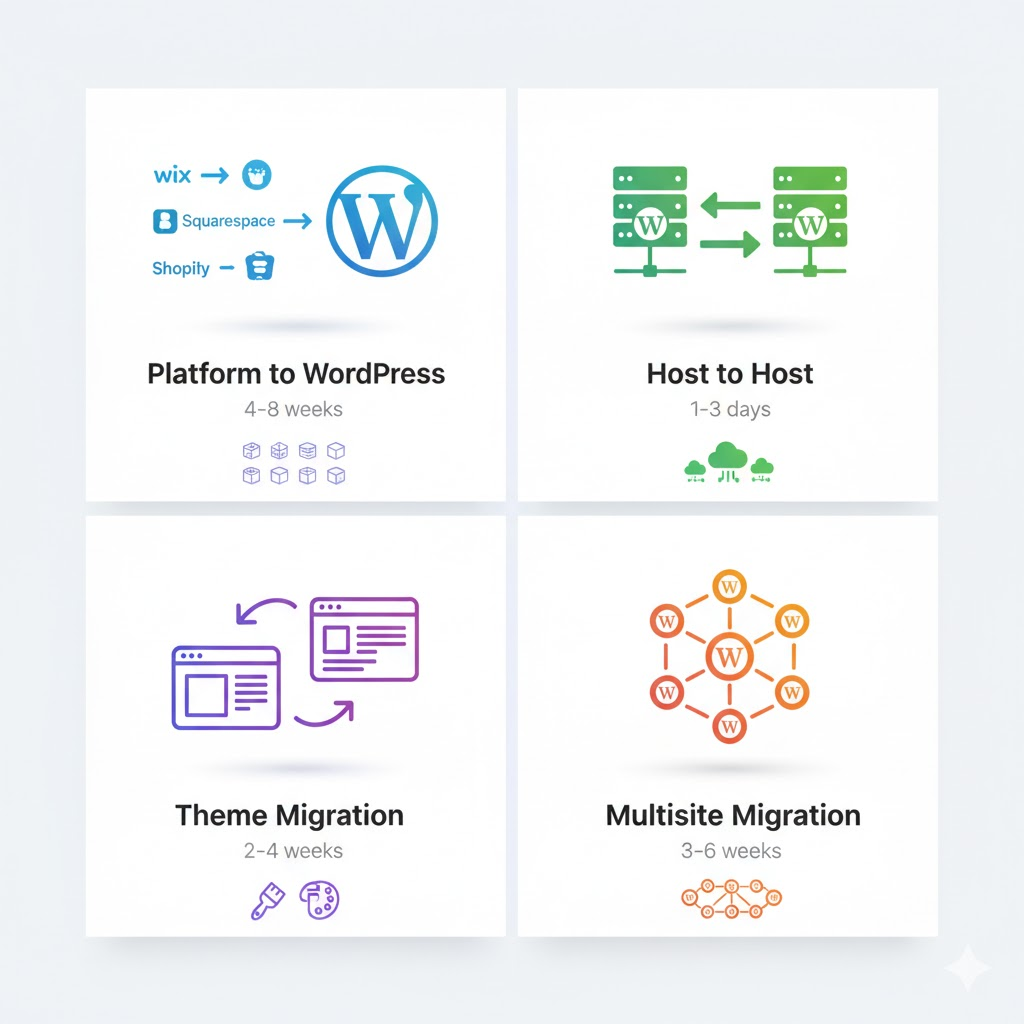
Platform-to-WordPress Migration
Moving from platforms like Wix, Squarespace, Shopify, or a custom CMS to WordPress. Specifically, this requires content extraction, restructuring, and rebuilding design elements.
Average Timeline: 4-8 weeks, depending on content volume
Common Challenges:
- Initially, different content structures require adaptation
- Next, proprietary features need WordPress alternatives
- Furthermore, URL structure changes require careful planning
- Finally, custom functionality needs rebuilding
Host-to-Host WordPress Migration
Transferring an existing WordPress site between hosting providers. Importantly, this is the simplest migration type.
Average Timeline: 1-3 days with minimal downtime
Common Challenges:
- First, DNS propagation delays can occur
- Additionally, database configuration differences arise
- Moreover, file permission issues may surface
- Lastly, the email configuration needs updating
Theme Migration
Changing WordPress themes while maintaining the same hosting and content. Notably, this affects both design and functionality.
Average Timeline: 2-4 weeks for complex customizations
Common Challenges:
- To begin with, widget compatibility issues emerge
- Subsequently, shortcode support differences appear
- In addition, custom post type integration is needed
- Ultimately, layout adjustments become necessary
WordPress Multisite Migration
Moving or consolidating multiple WordPress installations into a multisite network, or vice versa.
Average Timeline: 3-6 weeks, depending on site quantity
Common Challenges:
- Primarily, database restructuring complexity increases
- Secondly, user role management across sites is tricky
- Then, plugin compatibility across the network must be verified
- Finally, individual site configuration preservation is critical
Pre-Migration Requirements and Checklist
Essential Access Credentials Needed
Before starting any migration, gather these critical access points:
WordPress Admin Access:
- Dashboard login credentials
- Administrator-level privileges
- Access to all settings and configurations
Hosting Account Login:
- cPanel, Plesk, or custom hosting panel access
- Root or administrative server access
- File manager access
FTP/SFTP Credentials:
- File Transfer Protocol access
- Direct file management capability
- Server connection details (host, port, username, password)
Database Access:
- phpMyAdmin login credentials
- Direct MySQL database credentials
- Database name, username, and password
Domain Registrar Login:
- DNS management access
- Domain configuration settings
- Nameserver modification rights
Email Access:
- Ownership verification capability
- Important notification receipt
- Recovery email setup
Current Website Documentation
Create detailed documentation before starting migration:
Page Inventory:
- Complete list of all pages with URLs
- Content types and categories
- Page hierarchy and parent-child relationships
- Custom page templates in use
Post Inventory:
- Total number of posts
- All categories and subcategories
- Tag structure and taxonomy
- Custom taxonomies, if applicable
Media Library:
- Total images count and size
- Videos and multimedia content
- PDFs and downloadable files
- Other uploaded file types
Plugin List:
- All active plugins with version numbers
- Inactive plugins that may be needed
- Plugin dependencies and requirements
- Custom plugin configurations
User Roles:
- All user accounts and their email addresses
- Respective roles (Admin, Editor, Author, etc.)
- Permission levels and access rights
- Custom role definitions if any
Custom Post Types:
- Special content types beyond standard posts/pages
- Custom field configurations
- Templates associated with custom types
- Relationships between content types
Form Submissions:
- Backup of stored form data
- Lead information and customer inquiries
- Contact form configurations
- Integration settings with CRM
E-commerce Data:
- Products and product categories
- Customer orders and history
- Payment gateway configurations
- Shipping settings and rules
Technical Specifications to Record
Document these technical details for smooth migration:
Current WordPress Version:
- Check Dashboard → Updates
- Note exact version number
- Check for pending updates
PHP Version:
- Found in hosting control panel
- Also visible in System Status plugins
- Verify compatibility with target hosting
MySQL Version:
- Available in database management tools
- Check the phpMyAdmin dashboard
- Note database character set (UTF-8 recommended)
Server Type:
- Apache, Nginx, or other web server
- Server configuration details
- Rewrite rules and configurations
SSL Certificate Status:
- HTTP vs HTTPS configuration
- Certificate provider and expiry date
- Wildcard or single domain certificate
Current Hosting Provider:
- Account details and plan specifications
- Server location and resources
- Backup policies and retention
Domain Configuration:
- Current DNS settings
- Nameservers in use
- Propagation status and TTL settings
Step-by-Step WordPress Migration Process

Step 1: Create a Complete Backup
Never begin migration without a complete, verified backup. Above all, this is your safety net.
Using Plugins:
UpdraftPlus, BackupBuddy, or Duplicator can automate backups. First, install your chosen plugin. Then, configure backup location (cloud storage recommended). Finally, run a complete backup including files and the database. Learn more about 4 easy ways to back up your WordPress site.
Manual Backup Method:
Initially, download all files via FTP from your root directory. Next, export the database using phpMyAdmin (Export → SQL format → Download). Afterward, store both in a secure, accessible location.
Verification:
Subsequently, download backup files and verify they’re not corrupted. In particular, check file sizes match expectations.
Step 2: Prepare New Hosting Environment
Your destination hosting must meet WordPress’s minimum requirements.
Server Requirements:
- PHP Version: 7.4 or greater (8.0+ recommended for best performance)
- MySQL Version: 5.7 or greater, or MariaDB 10.3 or greater
- HTTPS Support: Valid SSL certificate for secure connections
- Memory: Minimum 512MB RAM (1GB+ recommended for better performance)
- Disk Space: Sufficient storage for your files and database
- Bandwidth: Adequate for your expected traffic levels
Environment Setup:
- Create new database in hosting control panel
- Note database name, username, and password securely
- Set up FTP/SFTP access credentials
- Configure PHP settings if needed:
- Memory limit (256MB recommended)
- Execution time (300 seconds for large imports)
- Upload file size (64MB+ for large media)
- Post max size (64MB+ for large content)
Step 3: Transfer Files and Database
This is the core technical migration step.
File Transfer:
- Upload all WordPress files to the new hosting via FTP/SFTP
- Include these critical directories:
wp-content(themes, plugins, uploads)wp-admin(WordPress admin files)wp-includes(core WordPress files)
- Maintain the exact directory structure from the original site
- Verify file permissions (644 for files, 755 for folders)
- Upload time depends on file size (typically 15-60 minutes)
- Use compression for faster transfer if possible
Database Import:
- Access phpMyAdmin on new hosting
- Select your newly created database
- Click the “Import” tab in top menu
- Choose your .sql backup file from local computer
- Click “Go” to start import process
- Verify table count matches original database
- Check for import errors or warnings
- Confirm all data imported successfully
Configuration Update:
- Locate and edit
wp-config.phpfile - Update these database credentials:
DB_NAME– Your new database nameDB_USER– Your new database usernameDB_PASSWORD– Your new database passwordDB_HOST– Usually ‘localhost’ (confirm with host)
- Save the updated file
- Upload to root directory if edited locally
- Keep backup of original wp-config.php
Step 4: Update URLs and Site Configuration
WordPress stores URLs in multiple database locations. These must be updated.
Using Search and Replace:
Better Search Replace plugin (free) handles this safely. Install on new site. Enter old URL (https://oldsite.com). Enter new URL (https://newsite.com). Select all tables. Run dry run first. Execute actual replacement.
Manual Database Update:
Run SQL queries in phpMyAdmin following MySQL best practices:
UPDATE wp_options SET option_value = replace(option_value, 'http://oldsite.com', 'http://newsite.com') WHERE option_name = 'home' OR option_name = 'siteurl';
UPDATE wp_posts SET guid = replace(guid, 'http://oldsite.com','http://newsite.com');
UPDATE wp_posts SET post_content = replace(post_content, 'http://oldsite.com', 'http://newsite.com');
UPDATE wp_postmeta SET meta_value = replace(meta_value,'http://oldsite.com','http://newsite.com');
Step 5: Configure DNS and Domain Settings
Point your domain to the new hosting server.
DNS Update Process:
Log in to the domain registrar account. Locate DNS management or nameserver settings. Update nameservers to the new hosting provider’s values. Save changes. DNS propagation takes 4-48 hours (usually 4-8 hours).
Testing During Propagation:
Use the hosts file to preview the new site before the DNS propagates. Edit the system hosts file with the new server IP. Verify everything works correctly. Remove the host file entry after DNS completes.
Step 6: Test Everything Thoroughly
Comprehensive testing prevents post-migration problems.
Functionality Checklist:
Test all navigation menus and internal links. Submit all contact forms and verify receipt. Test user registration and login processes. Verify that all images and media files display. Check that all plugins are activated and function properly. Test e-commerce checkout if applicable. Verify search functionality. Test all custom features and integrations.
Cross-Browser Testing:
Test in Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge. Verify mobile responsiveness on actual devices. Check tablet display and functionality.
Performance Testing:
Run Google PageSpeed Insights. Check GTmetrix for performance metrics. Verify load times under 3 seconds. Test from multiple geographic locations using WebPageTest.
Step 7: Implement SEO Preservation Measures
Protecting search rankings is critical during migration.
301 Redirects:
Map all old URLs to new equivalents. Implement via .htaccess or the Redirection plugin. Test each redirect manually. Verify proper HTTP status codes.
Submit Updated Sitemap:
Generate a new XML sitemap. Submit to Google Search Console. Submit to Bing Webmaster Tools. Verify sitemap is accessible and error-free. Follow Google’s site migration guidelines for best results.
Update Google Search Console:
Add a new domain property if the URL has changed. Verify ownership via DNS or HTML file. Update any structured data if modified. Monitor for crawl errors post-migration.
Step 8: Monitor Post-Migration Performance
Migration doesn’t end at launch. Monitoring is essential.
First 48 Hours:
Check the website every 2-3 hours. Monitor uptime using tools like UptimeRobot. Watch for error logs in the hosting panel. Respond immediately to any issues.
First 30 Days:
Track organic traffic in Google Analytics. Monitor keyword rankings. Check Google Search Console for crawl errors. Analyze user behavior for unusual patterns. Track conversion rates and goals.
WordPress Migration Timeline and Costs
Understanding both timeline and investment helps you plan effectively. Moreover, knowing what to expect prevents budget surprises.
Typical Migration Timeframes
Simple Host-to-Host Migration: Timeline: 1-3 days.
Complexity: Low
Best for: Small sites under 50 pages
Platform to WordPress Migration: Timeline: 4-8 weeks
Complexity: High
Best for: Moving from proprietary platforms
Importantly, each migration type requires different resources.
Complex Enterprise Migration: Timeline: 8-16 weeks
Complexity: Very high
Best for: Large sites over 500 pages with custom features
Migration Cost Breakdown
DIY Migration:
- Backup plugin: $0-$50 one-time or annual
- New hosting: $5-$50/month, depending on plan
- Tools and plugins: $0-$200 for premium options
- Domain transfer: $0-$15 if applicable
- Your time: Consider the hourly value of your time
- Total estimated cost: $5-$300 initial + ongoing hosting
Professional Migration Services:
- Basic migration: $500-$1,500
- Simple sites (under 50 pages)
- Standard hosting to hosting
- Minimal customization
- Basic testing included
- Standard migration: $1,500-$5,000
- Medium complexity (50-200 pages)
- Some custom features
- E-commerce functionality
- Comprehensive testing
- SEO preservation
- Complex migration: $5,000-$25,000+
- Large sites (200+ pages)
- Custom development required
- Multiple integrations
- Advanced functionality
- Extensive testing
- Performance optimization
- Enterprise migration: $25,000+
- Very large sites (500+ pages)
- Multiple custom features
- High-traffic requirements
- Complex data migration
- Team training included
- Extended support period
Hidden Costs to Consider:
- Downtime costs: Potential revenue loss during migration
- Testing time: Internal team hours for QA
- Training time: Staff learning the new WordPress environment
- Premium themes: $30-$200 if theme purchase needed
- Premium plugins: $50-$500/year for essential tools
- Performance optimization: May require additional work
- SEO monitoring: Tools and time to track rankings
- Content updates: Fixing issues discovered post-migration
- Emergency fixes: Budget for unexpected problems
Common WordPress Migration Problems and Solutions
[IMAGE 5: WordPress Migration Troubleshooting Guide – See image prompts below]
Even with careful planning, migration issues can arise. However, most problems have straightforward solutions.
Problem 1: White Screen of Death
Symptoms:
- A blank white page appears instead of the website
- No error messages visible
- Cannot access the admin dashboard
Causes:
- PHP memory limit exceeded
- Plugin conflicts are causing fatal errors
- Corrupted .htaccess file
- PHP version incompatibility
Solutions:
Increase PHP memory limit in wp-config.php:
define('WP_MEMORY_LIMIT', '256M');
Additional troubleshooting steps:
- Disable all plugins via database or FTP
- Rename plugins folder temporarily
- Rename .htaccess file to .htaccess-old
- Check PHP error logs for specific errors
- Switch to default WordPress theme
Problem 2: Images Not Displaying
Symptoms:
- Broken image icons instead of actual images
- Some images show, others don’t
- Thumbnails missing
Causes:
- Incorrect file paths in database
- Missing media files in wp-content/uploads
- Incorrect file permissions
- URLs not updated properly
Solutions:
- Verify all files uploaded to wp-content/uploads
- Check file permissions (644 for files, 755 for folders)
- Run search-replace on image URLs
- Regenerate thumbnails using plugin
- Clear CDN cache if applicable
Problem 3: Permalinks Not Working (404 Errors)
Symptoms:
- All pages except homepage show 404 errors
- Clicking links returns “Page Not Found”
Causes:
- .htaccess file missing or incorrect
- Mod_rewrite not enabled on server
- Permalink settings not saved
Solutions:
- Go to Settings → Permalinks in WordPress dashboard
- Simply click “Save Changes” without modifying
- Check if .htaccess exists in root directory
- Contact hosting to enable mod_rewrite if necessary
See our guide on fixing redirect issues after WordPress migration.
Problem 4: Database Connection Error
Symptoms:
- “Error establishing database connection” message
- Cannot access any pages
Causes:
- Incorrect wp-config.php credentials
- Database server not running
- Corrupted database tables
Solutions:
- Verify database credentials in wp-config.php
- Contact hosting to confirm database is running
- Check database user has proper privileges
- Repair database tables using wp-config.php:
define('WP_ALLOW_REPAIR', true);
Problem 5: Mixed Content Warnings (HTTP/HTTPS)
Symptoms:
- Browser shows “Not Secure” warning despite SSL
- Padlock icon broken or missing
Causes:
- Some resources loading via HTTP instead of HTTPS
- Database still contains old HTTP URLs
Solutions:
- Update WordPress Address and Site Address to HTTPS
- Run search-replace changing HTTP to HTTPS
- Force HTTPS in .htaccess:
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} off
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ https://%{HTTP_HOST}%{REQUEST_URI} [L,R=301]
SEO Considerations During WordPress Migration
Preserving Search Rankings
Search engine rankings represent significant business value. Proper migration protects this investment.
Pre-Migration SEO Audit:
- Document current rankings for top keywords
- Export all existing metadata (titles, descriptions)
- Map the URL structure completely
- Identify high-value pages receiving the most traffic
- Document all inbound links
- Screenshot current search console data
During Migration:
- Maintain an identical URL structure when possible
- Implement 301 redirects for any URL changes
- Preserve all metadata exactly
- Keep the same site architecture and internal linking
- Maintain XML sitemap structure
- Don’t change URLs unnecessarily
Post-Migration Verification:
- Submit the new sitemap to search engines
- Monitor Google Search Console for errors
- Track rankings for key terms weekly
- Check inbound links still work properly
- Monitor organic traffic patterns
- Watch for crawl errors
URL Structure Best Practices
Maintaining URLs:
- Keep the existing permalink structure if SEO-friendly
- Preserve custom URL slugs
- Maintain category and tag URLs
- Keep date-based archives if used
Changing URLs (If Necessary):
- Create a comprehensive redirect map
- Implement 301 redirects (permanent)
- Avoid 302 redirects (temporary)
- Test every redirect individually
- Monitor 404 errors continuously
Redirect Implementation:
Via .htaccess (Apache servers):
Redirect 301 /old-page/ https://newsite.com/new-page/
Via the Redirection plugin (easier for many redirects). Via Cloudflare Page Rules (for large sites).
Schema Markup and Structured Data
Preservation:
Export existing schema markup. Verify schema transfers correctly. Test with Google Rich Results Test. Update the organization schema with new URLs. Maintain breadcrumb structured data.
Enhancement Opportunities:
Add FAQ schema for question sections. Implement the Article schema for blog posts. Use the Review schema for testimonials. Add LocalBusiness schema if applicable. Reference Schema.org for proper implementation.
Performance Optimization Post WordPress Migration
Migration provides an opportunity to improve website performance significantly. Following WordPress security best practices protects your optimized site.
Image Optimization
Techniques:
Compress all images using ShortPixel or Imagify. Implement lazy loading for below-fold images. Use WebP format with fallbacks. Properly size images for display dimensions. Remove unused images from the media library.
Expected Impact: 30-50% reduction in page size, 40-60% faster load times for image-heavy pages.
Caching Implementation
Caching Layers:
Browser caching via .htaccess headers. Page caching using WP Rocket or W3 Total Cache. Object caching using Redis or Memcached. CDN caching via Cloudflare or similar.
Configuration:
Set browser cache expiration (1 year for static assets). Enable page cache with mobile detection. Configure object cache for database queries. Implement CDN for global content delivery.
Expected Impact: 50-70% reduction in server response time, 60-80% faster repeat visits.
Database Optimization
Maintenance Tasks:
Remove post revisions (or limit to 5). Delete spam and trash comments. Clean transient options. Remove unused tables from old plugins. Optimize database tables.
Using Plugins:
WP-Optimize automates database cleaning. Set weekly automatic optimization. Remove orphaned metadata. Clean expired transients.
Manual Optimization:
DELETE FROM wp_posts WHERE post_type = 'revision';
DELETE FROM wp_comments WHERE comment_approved = 'spam';
OPTIMIZE TABLE wp_posts, wp_comments, wp_options;
Expected Impact: 20-40% smaller database size, 15-25% faster query execution.
Code Minification and Compression
Implementation:
Minify CSS files (remove whitespace and comments). Minify JavaScript files. Combine multiple CSS files when possible. Enable GZIP compression on server. Use HTTP/2 for improved loading.
Tools:
Autoptimize for automated minification. WP Rocket for comprehensive optimization. Cloudflare for compression and delivery.
Expected Impact: 40-60% reduction in file sizes, 25-35% faster page loads.
For ongoing optimization, consider implementing A/B testing on WordPress to continuously improve conversion rates.
Security Considerations After WordPress Migration
Immediate Security Actions
Essential Tasks:
Change all passwords (WordPress admin, database, FTP). Update security keys in wp-config.php. Install security plugin (Wordfence or Sucuri). Enable two-factor authentication. Disable file editing in the dashboard.
Security Configuration:
// Add to wp-config.php
define('DISALLOW_FILE_EDIT', true);
define('FORCE_SSL_ADMIN', true);
For advanced server configurations, refer to Apache documentation for .htaccess optimization.
Ongoing Security Maintenance
Regular Tasks:
Update WordPress core immediately when available. Update plugins within 48 hours of releases. Update themes regularly. Run security scans weekly. Monitor login attempts and blocks. Review user accounts quarterly.
Backup Schedule:
Daily automated backups (retain 30 days). Weekly manual verification. Store backups off-site. Test the restoration process quarterly.
Tools and Plugins for WordPress Migration
Migration-Specific Plugins
All-in-One WP Migration: Best for: Beginners and simple migrations.
Pros: User-friendly interface, one-click migration
Cons: File size limitations on the free version
Cost: Free (Premium from $69)
Duplicator: Best for: Complete site cloning Pros: Reliable, extensive documentation Cons: Learning curve for beginners Cost: Free (Premium from $69)
WP Migrate DB: Best for: Database migrations Pros: Specialized database handling Cons: Requires separate file transfer Cost: Free (Premium from $99)
BlogVault: Best for: Automated migrations with safety
Pros: Staging environment included, automatic backups
Cons: Subscription required
Cost: From $89/year
Essential Post-Migration Plugins
Performance:
WP Rocket ($49/year) – Comprehensive caching solution,
Imagify ($9.99/month) – Image optimization,
Query Monitor (Free) – Debug performance issues
SEO:
Yoast SEO (Free) – Complete SEO management
Redirection (Free) – Manage 301 redirects XML
Sitemap (Free) – Generate sitemaps
Security:
Wordfence (Free) – Security scanning and firewall
UpdraftPlus (Free) – Automated backups iThemes
Security (Free) – Security hardening
When to Hire Professional WordPress Migration Services
Professional Migration Decision Framework
Consider DIY When:
Your site has fewer than 50 pages. You have technical experience with WordPress. Timeline is flexible (can handle delays). Budget is very limited (under $500). The site has simple functionality (no custom features). Traffic is low (downtime less critical).
Hire Professionals When:
The site has over 100 pages and a complex structure. E-commerce functionality requires preservation. High traffic makes downtime costly. Lack technical WordPress experience. Need SEO rankings protected carefully. Custom functionality requires migration. Timeline is tight and critical. Budget allows ($1,500+ available). Professional WordPress development services provide experienced handling of complex migrations.
What Professional WordPress Development Services Include
Standard Migration Package:
Complete backup and restoration. File and database transfer. URL updates and configuration. Plugin compatibility check. Basic testing and verification. DNS configuration assistance. Post-migration support (7-30 days).
Premium Migration Package:
Everything in the standard package plus performance optimization. Security hardening. SEO preservation strategy. Custom feature migration. Design improvements. A/B testing and conversion optimization infrastructure. Training and documentation. Extended support (30-90 days).
Testing Checklist for WordPress Migration
Before launching your migrated site, comprehensive testing is essential. In fact, thorough testing prevents costly post-launch problems.
Pre-Launch WordPress Migration Testing Requirements
Functionality Testing:
☐ Navigation & Links
- First and foremost, all pages load without errors
- Additionally, all internal links work correctly
- Moreover, the menu navigation functions properly
- Similarly, breadcrumbs display accurately
☐ Media & Content
- Equally important, all images display properly without broken links
- Furthermore, videos play correctly
- In addition, downloads work as expected
- Likewise, content formatting is preserved
☐ Forms & Interactions
- Contact forms submit successfully
- Form validation works properly
- Email notifications are sent correctly
- Spam protection active
☐ User Features
- Search functionality works
- User registration and login functionality
- Password reset emails sent
- Comments can be posted and approved
☐ Admin Functions
- The admin dashboard is fully accessible
- All plugins activate without errors
- The theme customizer works properly
- Media upload functions correctly
☐ Custom Elements
- Custom post types display correctly
- Custom fields populate properly
- Shortcodes render accurately
- Widgets appear in the correct locations
E-commerce Testing (If Applicable):
☐ Product Pages
- Product pages display correctly
- Images and galleries work
- Pricing displays accurately
- Product variations function
☐ Shopping Cart
- Add to cart functionality works
- Cart updates correctly
- Quantity changes apply
- Remove items works
☐ Checkout Process
- Checkout page loads properly
- All checkout fields present
- Shipping calculations correct
- Tax calculations accurate
☐ Payment & Orders
- Payment gateways connect successfully
- Test transaction process
- Order confirmations send
- Inventory tracking works
- Customer accounts function
Mobile Responsiveness:
☐ Mobile Navigation
- The menu works on mobile devices
- Hamburger menu functions
- Touch interactions responsive
☐ Mobile Layout
- Images scale properly
- Text is readable without zooming
- No horizontal scrolling
- Content stacks correctly
☐ Mobile Forms
- Forms usable on mobile
- Input fields are appropriately sized
- Buttons easily tappable
- Virtual keyboard doesn’t break layout
Performance Testing:
☐ Speed Metrics
- Google PageSpeed score above 80
- Load time under 3 seconds
- Time to Interactive under 5 seconds
- All Core Web Vitals pass
- No render-blocking resources
☐ Cross-Browser Testing
- Test in Chrome (latest version)
- Test in Firefox (latest version)
- Test in Safari (Mac/iOS)
- Test in Edge (latest version)
- Test on actual mobile devices
SEO Testing:
☐ Technical SEO
- All 301 redirects are working correctly
- XML sitemap generates properly
- Robots.txt file present and correct
- SSL certificate active (HTTPS)
- No mixed content warnings
☐ On-Page SEO
- Meta titles preserved or improved
- Meta descriptions present
- Header tags (H1, H2, etc.) correct
- Image alt text preserved
- Structured data validates
☐ Search Console
- No broken external links
- No 404 errors reported
- Mobile usability passes
- Index coverage shows no errors
Security Testing:
☐ Security Basics
- SSL certificate is active and valid
- HTTPS is forced on all pages
- Login page secured
- Admin area protected
☐ File Security
- File permissions correct (644/755)
- No unnecessary files exposed
- Debug mode disabled
- Error reporting off in production
☐ Plugin Security
- All plugins updated to the latest versions
- Vulnerable plugins removed
- Security plugin active
- Firewall configured properly
WordPress Migration Post-launch Monitoring and Optimization
Critical Metrics to Track
Traffic Metrics:
Organic search traffic (via Google Analytics). Direct traffic patterns. Referral traffic sources. Social media traffic. Overall sessions and users. Bounce rate by page. Average session duration.
SEO Performance:
Keyword rankings for top terms. Impressions in Google Search Console. Click-through rates. Crawl errors and issues. Index coverage. Page load speed. Mobile usability errors.
Conversion Metrics:
Form submission rates. Newsletter signups. Purchase completions (e-commerce). Goal completions. Conversion rate by traffic source. Revenue per visitor.
Technical Performance:
Server response time. Page load time. Time to First Byte. First Contentful Paint. Largest Contentful Paint. Cumulative Layout Shift. First Input Delay.
30-Day Post-Migration Action Plan
Days 1-7: Intensive Monitoring
Check the site multiple times daily. Respond to any reported issues immediately. Monitor uptime continuously. Track error logs. Review analytics daily. Address any 404 errors.
Days 8-14: Performance Analysis
Compare pre-migration vs. post-migration metrics. Identify any ranking changes. Analyze traffic patterns. Assess user behavior changes. Document performance improvements.
Days 15-21: Optimization Phase
Implement performance improvements. Fix any identified issues. Optimize slow-loading pages. Improve conversion paths. Address user feedback.
Days 22-30: Long-term Planning
Develop an ongoing optimization roadmap. Plan A/B testing strategy. Document lessons learned. Create a maintenance schedule. Plan future improvements.
WordPress Migration Best Practices Summary
Critical Success Factors
- Always Create Complete Backups: Never start without verified backups of files and the database
- Test in Staging Environment: Use the staging site to identify issues before going live
- Implement Proper Redirects: Protect SEO with comprehensive 301 redirect mapping
- Verify Everything Thoroughly: Test all functionality across browsers and devices
- Monitor Post-Migration: Track metrics closely for the first 30 days
- Communicate Timeline Clearly: Set realistic expectations with stakeholders
- Document Everything: Maintain detailed records of all changes
- Prioritize Security: Update passwords, plugins, and implement security measures immediately
- Optimize Performance: Use migration as an opportunity to improve speed
- Plan for Contingencies: Have a rollback plan if serious issues occur
Common Migration Mistakes to Avoid
- Skipping Backups: Always back up before starting any migration work
- Not Testing Redirects: Broken redirects destroy SEO rankings permanently
- Ignoring Mobile: Test mobile experience thoroughly, not just desktop
- Forgetting Email: Configure email properly, or notifications won’t send
- Rushing Launch: Take time to test everything thoroughly before going live
- Not Monitoring: Post-launch issues multiply if not caught quickly
- Inadequate Planning: Poor planning leads to unexpected problems
- Wrong Timing: Avoid migrations during peak business periods
- Insufficient Resources: Allocate appropriate time, budget, and expertise
- No Rollback Plan: Always have the ability to revert if critical issues arise
Conclusion
To begin, start with complete documentation of your current site. Next, create verified backups. Then, develop a detailed migration plan. After that, execute systematically following web development best practices. Subsequently, test exhaustively. Finally, monitor continuously after launch.
With a proper approach, WordPress migration minimizes risk while maximizing opportunity for improvement. Ultimately, your website emerges faster, more secure, more flexible, and better positioned for growth.
For comprehensive WordPress migration services or to explore more WordPress tips and guides, professional assistance is available. Get a custom migration quote tailored to your specific needs.
Helpful for: Website owners, developers, and marketing teams planning WordPress migration projects